Magnetotellurics

The magnetotellurics method uses variations of natural electromagnetic fields to map the electrical conductivity distribution in the lithosphere. The sources of these field variations lie in the Earth's exterior in the ionosphere and the magnetosphere.
Deposits develop in the context of geological formation conditions, which in their entirety are referred to as a mineral system. Magnetotelluric measurements for the exploration of the lithosphere provide important information for the identification and characterisation of mineral systems. We are also interested in dynamic processes in the continental lithosphere, which can lead to volcanism or large-scale uplift far from plate tectonic boundaries. Our magnetotelluric work has focussed on Mongolia for several years. Since 2016, our magnetotelluric work has focussed on Mongolia. The working group has been conducting measurements to investigate the structure of the Earth's crust and upper mantle beneath the Hangai mountains and the Gobi-Altai region, with the aim of gaining a better understanding of the present deformation processes far from tectonic plate boundaries, prevailing intraplate volcanism and intracontinental earthquake zones.
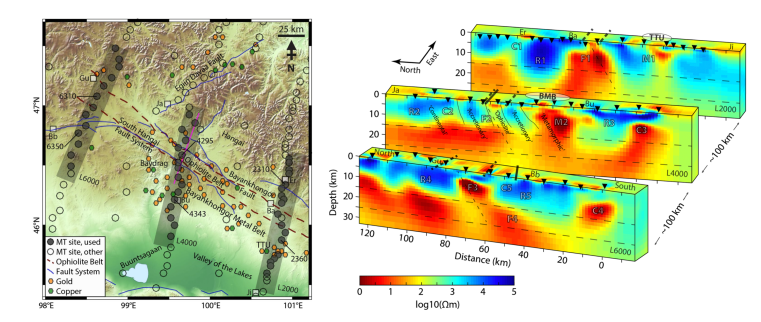
Shown here is a crustal resistivity model across the Bayankhongor Metal Belt, Mongolia, derived from three-dimensional magentotelluric inversion. The study suggests that processes leading to the formation of the mineralization zone are deeply rooted and inherited in the present-day lithospheric structure (modified after: Comeau et al., 2021).
More on this topic can be found in the project overview.

