Consider first a one-dimensional PDE for the unknown function 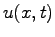 .
One way to numerically solve the PDE is to approximate all the derivatives by finite differences. We partition the domain in space using a mesh
.
One way to numerically solve the PDE is to approximate all the derivatives by finite differences. We partition the domain in space using a mesh
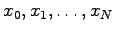 and in time using a mesh
and in time using a mesh
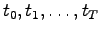 . We assume first a uniform partition both in space and in time, so the difference between two consecutive space points will be
. We assume first a uniform partition both in space and in time, so the difference between two consecutive space points will be
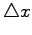 and between two consecutive time points will be
and between two consecutive time points will be
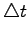 , i.e.,
, i.e.,
Subsections
Gurevich_Svetlana
2008-11-12