We now prove convergence of the iterative method for linear equations
where ![]() are linear bounded operators. To avoid purely technical difficulties we assume F and
are linear bounded operators. To avoid purely technical difficulties we assume F and ![]() to be of finite dimension. The iteration reads
to be of finite dimension. The iteration reads
We note in passing that for dim ![]() this is just the Kaczmarz method.
this is just the Kaczmarz method.
Proof: For ![]() this is just Theorem 3.9 of [3]. Our proof is a slight extension of this result.
this is just Theorem 3.9 of [3]. Our proof is a slight extension of this result.
To begin with we write ![]() in the form
in the form
with certain vectors ![]() . Inserting this into the recursion (4.2) yields
. Inserting this into the recursion (4.2) yields
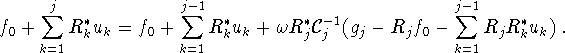
We apply ![]() . After obvious manipulations we obtain
. After obvious manipulations we obtain
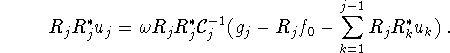
Hence,
Now let A be the operator ![]() and R the map
and R the map ![]() , i.e.
, i.e. ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() where D is the (block) diagonal and L the (block) lower left part of A. Let the vectors u, g consist of the components
where D is the (block) diagonal and L the (block) lower left part of A. Let the vectors u, g consist of the components ![]() ,
, ![]() , resp. and let
, resp. and let ![]() be the (block) diagonal
be the (block) diagonal ![]() . Then (4.5) reads
. Then (4.5) reads
![]()
or
Using (4.4) with j = p we see that
Now assume that ![]() range
range ![]() . Then,
. Then, ![]() for all iterates, and (4.6)-(4.7) yield
for all iterates, and (4.6)-(4.7) yield
![]()
or
![]()
Hence
We show that all the eigenvalues of ![]() are either 1 or less than 1 in absolute value if
are either 1 or less than 1 in absolute value if ![]() ,
, ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be such an eigenvalue and u the corresponding eigenvector, i.e.
be such an eigenvalue and u the corresponding eigenvector, i.e.
![]()
or
![]()
Using ![]() yields
yields
Now let (u,Du) = 1 and ![]() ,
, ![]() with
with ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() real. (4.9) immediately yields
real. (4.9) immediately yields
![]()
hence
![]()
Since ![]() we have
we have ![]() , and since
, and since ![]() we have
we have ![]() . For
. For ![]() we have
we have ![]() . For
. For ![]() we have
we have ![]() provided that
provided that ![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() for
for ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Returning to (4.8) we see that the sequence ![]() converges except in the eigenspace of
converges except in the eigenspace of ![]() for the eigenvalue 1. But this eigenspace is identical to the null space of
for the eigenvalue 1. But this eigenspace is identical to the null space of ![]() . This does not prevent the
. This does not prevent the ![]() from converging.
from converging.
![]()