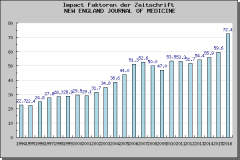
Zeitlicher Verlauf der Impact Faktoren für das Journal „New England Journal of Medicine“ (Anklicken zum Vergrössern)
Die Impact Faktoren 2016 für über 8.863 Zeitschriften stehen ab sofort (zusätzlich zu dem Web-Angebot) auch unter der gewohnten Adresse https://www.uni-muenster.de/ZBMed/recherche/zeitschriften/impact-faktoren.html zur Verfügung (nur innerhalb des Hochschulnetz). Zusätzlich zur Suche beim „original“ InCites(TM) Journal of Citation Reports(R) zeigt Ihnen diese Webseite die Klasseneinteilung der Journale an, was wichtig für die Habilitation ist.
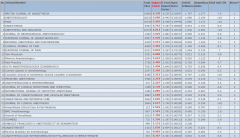
Klasseneinteilung der Category Anesthesiology (Klicken zum Vergrössern)
Die obige Tabelle zeigt drei zusätzliche Parameter an, die für Sie interessant sein könnten:
- The 5-year journal Impact Factor is the average number of times articles from the journal published in the past five years have been cited in the JCR year. It is calculated by dividing the number of citations in the JCR year by the total number of articles published in the five previous years. The 5-Year Journal Impact Factor measurement is the same as the Journal, but with three more years added to both the numerator and the denominator. Instead of a two-year window, it is a five-year window. In the 2015 JCR, the five-year window will include 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 & 2014. The calcuation is factored in the same mannner as the Journal Impact Factor, but considers a five-year window of citation data. The 5-Year Journal Impact Factor provides a broader view onto the citation data, but at the expense of granularity (which is reduced). Like the the Journal Impact Factor, the 5-Year Journal impact Factor is a publication-level metric. It does not apply to individual papers or subgroups of papers that appeared in the publication. Additonally, it does not apply to authors of papers, research groups, institutions, or universities. Also, note that the typical lag after publication of a paper until peak citation is variable (across papers, across time, across publications, and across domains). When the lag is greater than two years (which it often is), a publication’s 5-year Journal Impact Factor will tend to be higher than its Journal Impact Factor Also, Journal Impact Factor and 5-year Journal Impact Factor will typically be identical for the first two years that a publication is covered in the JCR.
- Eigenfactor: Eine kostenfreie Alternative zu der Thomson Reuters Zitierungsdatenbank „Journal Citation Reports“, die auch die Zitierungen durch Zeitungen etc. bewertet. Nicht korrigiert gegen Artikelzahl.
- Article Influence: Eigenfactor dividiert durch die Anzahl der Artikel einer Zeitschrift, ist somit vergleichbar mit dem Impact Factor. The Article Influence determines the average influence of a journal’s articles over the first five years after publication. It is calculated by multiplying the Eigenfactor by 0.01 and dividing by the number of articles in the journal, normalized as a fraction of all articles in all publications. This measure is roughly analogous to the 5-Year Journal Impact Factor in that it is a ratio of a journal’s citation influence to the size of the journal’s article contribution over a period of five years. The equation is as follows: (0,01 * Eigenfactor score) / X where X = 5-year Journal Article Count divided by the 5-year Article Count from All Journals. The mean Article Influence for each article is 1.00. A score greater than 1.00 indicates that each article in the journal has above-average influence. A score less than 1.00 indicates that each article in the journal has below-average influence.
Bitte denken Sie daran, dass die Impact Faktoren der Social Sciences Titel nur unter https://jcr.incites.thomsonreuters.com/ zu finden sind.
