 |


![]()
Name: Dr. Panupun Limpachayaporn
Diploma / M.Sc degree: Georg-August-University Göttingen, Germany
(October 2008)
PhD Project: Synthesis of New Potential Radiotracers for Molecular Imaging of Apoptosis
Abstract of Research Project
"Apoptosis" or programmed cell death is a regulated destruction of excess, damaged and potentially dangerous cells in order to protect itself from rogue cell as well as to strictly control the number of cells and tissue size in organisms while new cells are generated through mitosis cell division in every moment. Biological and morphological changes recognized as apoptosis are caused by a set of cysteine aspartyl-specific proteases known as “caspases” which over a dozen has been identified in human. They are homologous to each other, but play different roles in apoptotic pathway. However, too much or too little apoptosis might lead to neurodegenerative diseases (such as stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, etc.), cardiovascular diseases (such as myocardial ischemia and congestive heart failure) including developmental defects. Possible medical treatment needs to tightly monitor the apoptosis, therefore, caspases are our therapeutic biological targets, in particular, executing caspase-3 and caspase-7 which are applicable to hinder apoptosis.
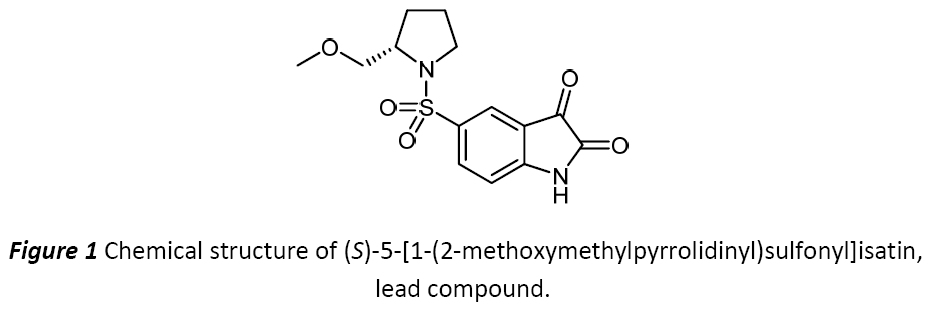
The main purpose of the project is to synthesize new fluorinated analogues of (S)-5-[1-(2-methoxymethylpyrrolidinyl)sulfonyl]isatin, the lead compound depicted in Figure 1, in order to enhance the inhibitory activity selectively against caspase-3 and caspase-7. Besides new therapeutic properties studied by Structure-Activity Relationship (SARS), fluorinated, methylated and iodinated analogues will allow us to prepare new potential radiotracers in order to visualize and characterize biological processes at molecular level of apoptosis by the in vivo molecular imaging using Positron Emission Tomography (PET) or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT).
Publications
P. Limpachayaporn, S. Wagner, K. Kopka, S. Hermann, M. Schäfers, G. Haufe
Synthesis, 18F–Radiolabeling, and in Vivo Biodistribution Studies of N–Fluorohydroxybutyl Isatin Sulfonamides using Positron Emission Tomography
J. Med. Chem. 56 (2013), 4509-4520.
P. Limpachayaporn, B. Riemann, K. Kopka, O. Schober, M. Schäfers, G. Haufe
Influence of 4- or 5-substituents on the pyrrolidine ring of 5-[1-(2-methoxymethylpyrrolidinyl)sulfonyl]isatin derivatives on their inhibitory activities towards caspases-3 and -7
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 64 (2013) 562-578.
P. Limpachayaporn, M. Schäfers, O. Schober, K. Kopka, G. Haufe
Synthesis of new fluorinated, 2-substituted 5-pyrrolidinylsulfonyl isatin derivatives as caspase-3 and caspase-7 inhibitors: Nonradioactive counterparts of putative PET-compatible apoptosis imaging agents
Bioorg. Med. Chem. 21 (2013), 2025–2036.
Panupun Limpachayaporn
eMail: Panupun Limpachayaporn